The CHIASMA project, under Horizon Europe, aims to redefine the safety and sustainability assessment of chemicals and materials through the development of innovative New Approach Methodologies (NAMs). The project addresses critical regulatory needs by creating a robust framework that integrates experimental and computational approaches while adhering to principles of sustainability, ethics, and practicality. By replacing traditional animal-based testing with advanced tools, CHIASMA aligns with the EU’s Safe and Sustainable by Design (SSbD) framework and broader sustainability initiatives such as the European Green Deal. The project focuses on three key chemical and material groups — PFAS, (nano-)pesticides, and 2D materials for energy applications — ensuring that its methodologies are relevant to real-world challenges and regulatory demands.
The Consortium
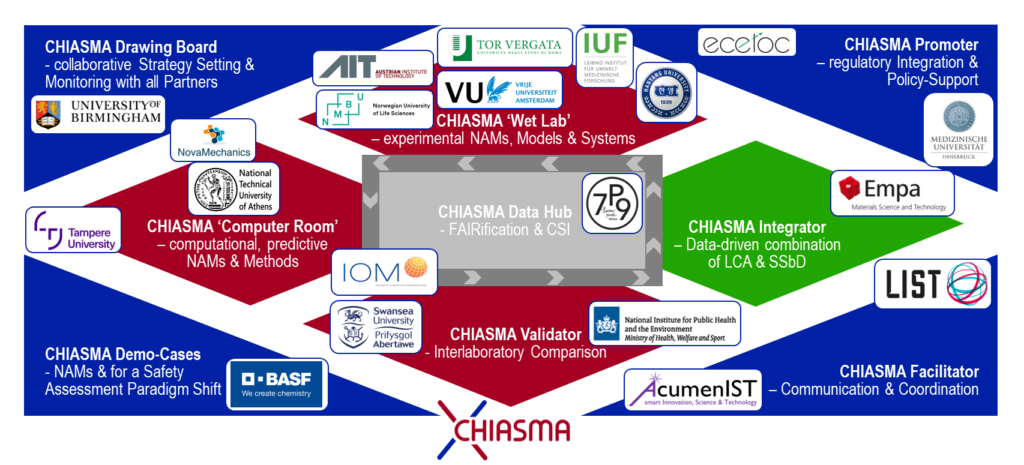
The CHIASMA consortium is a carefully selected group of leading institutions from academia, industry, and regulatory bodies across Europe and beyond. This multidisciplinary team includes 20 partners from 12 countries, coordinated by the Luxembourg Institute of Technology (LIST). The consortium combines expertise in computational modeling, advanced in vitro and ex vivo testing methods, regulatory science, and sustainability assessments. Key contributors include renowned universities, as well as prominent research. Industrial partners, bring real-world application perspectives, while regulatory-focused entities ensure alignment with current legislative frameworks. This consortium’s structure allows CHIASMA to integrate cutting-edge science with practical applications, enabling the development of tools that are both innovative and accessible to stakeholders.
The R&I Approach
CHIASMA employs an integrated and iterative methodology designed to address safety and sustainability from multiple angles. The project combines chemocentric, biocentric, and experimental approaches within a comprehensive assessment framework. Chemocentric methods utilize AI-powered models, QSAR tools, and knowledge graphs to analyze and predict chemical properties, while also identifying gaps in existing data. Biocentric models, such as PBK and AOP frameworks, offer detailed insights into biological mechanisms and toxicity pathways. Where data gaps remain, CHIASMA deploys experimental NAMs, including advanced in vitro and human ex vivo models, as well as non-mammalian in vivo systems like fish embryos.
The Aims & Objectives
CHIASMA’s overarching aim is to create a robust framework for safety and sustainability assessments that can be widely adopted by regulators and industry. This ambition is supported by eight high-level objectives (HLOs), each tied to concrete goals:
- Interface Communities and Regulatory Relevance: CHIASMA aims to engage regulatory bodies, industry, and academia to ensure the NAMs it develops are aligned with practical and legislative needs. It plans to organize at least two Risk Assessor Summits, foster collaborations across sectors, and deliver a strategic engagement roadmap that enhances the uptake of NAMs.
- Demonstrating NAM Utility for REACH and CLP: The project will refine and validate NAMs to meet regulatory needs, focusing on endpoints critical for human and environmental safety. CHIASMA intends to develop at least 14 NAMs (8 computational and 6 experimental), each targeting specific biological endpoints such as genotoxicity, endocrine disruption, and inflammation. These NAMs will also support Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment (IATAs), enabling comprehensive safety evaluations.
- Long-term Safety Assessment: To address chronic conditions such as neurotoxicity and developmental toxicity, CHIASMA will develop mechanistically anchored tools capable of predicting long-term effects. High-throughput kits for transcriptomics and epigenetics will be created to facilitate cost-effective, large-scale testing.
- User-friendly Interfaces: The project will develop a digital interface that integrates the CHIASMA framework, enabling users to execute safety assessments efficiently. This interface will include detailed documentation and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to ensure transparency and usability.
- NAM Transferability: CHIASMA will validate the transferability of its NAMs by conducting inter-laboratory comparisons. At least one comparison test will be conducted for each NAM, ensuring reproducibility across different settings and enhancing regulatory acceptance.
- Trans-domain Applicability: The CHIASMA framework will be tested across the three demonstration cases, proving its versatility and applicability to diverse chemical and material types. These tests will involve mock regulatory dossiers to evaluate real-world applicability.
- Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA) Enhancements: CHIASMA will refine the USEtox model to allow the use of in vitro and in silico data for characterizing human and ecotoxicity impacts. This will improve the integration of toxicity data into sustainability assessments, facilitating more comprehensive environmental impact evaluations.
FAIR-ification and GLP-ification: CHIASMA will ensure all methodologies adhere to FAIR and GLP principles, making data accessible, reproducible, and regulatory-ready. Protocols will be prepared for submission to international standardization bodies, supporting the global adoption of NAMs.

The Impact
CHIASMA is poised to make a significant impact across scientific, regulatory, and industrial domains. The project directly supports the EU’s vision for a toxic-free and sustainable society by providing ethical, non-animal testing alternatives that meet stringent regulatory standards. Its focus on sustainability ensures that the developed methodologies contribute to the broader goals of the European Green Deal and the Advanced Materials Initiative 2030.
From a scientific perspective, CHIASMA aims to advance the state of the art in toxicity and sustainability assessment, fostering innovation in computational and experimental methods. These advancements will empower regulators and industries with tools to make more informed decisions about the safety and sustainability of materials and chemicals. The project’s methodologies are expected to reduce the reliance on animal testing, addressing ethical concerns while streamlining the regulatory approval process.
Industrially, CHIASMA’s tools will enable companies to design safer and more sustainable products, giving European industries a competitive edge in the global market. The project’s focus on regulatory relevance ensures that its outcomes will be immediately applicable, facilitating smoother transitions to compliance with evolving legislation. Additionally, CHIASMA’s methodologies will help industries anticipate and mitigate risks associated with new and existing materials, promoting long-term sustainability and innovation.
CHIASMA actively engages with other EU and international initiatives to ensure alignment and maximize its impact. The project builds on the EU’s Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability and collaborates with frameworks such as the Partnership for the Assessment of Risks from Chemicals (PARC). It also interfaces with the OECD’s ongoing efforts to develop and validate alternative testing methods, contributing to global standardization and regulatory harmonization.
The consortium maintains close ties with projects addressing similar goals, such as NanoHarmony and RiskGONE, which focus on nanosafety, and MACRAMÉ, which explores hazard assessment methods for advanced materials. Through these connections, CHIASMA ensures the integration of its findings into broader scientific and regulatory contexts, fostering knowledge exchange and avoiding duplication of efforts. Engagement with European and international regulatory bodies, including ECHA, EFSA, and the US EPA, further enhances the project’s relevance and applicability.
By bridging diverse fields and fostering collaboration across sectors, CHIASMA exemplifies a holistic approach to advancing safety and sustainability. Its integration with complementary initiatives ensures that its outcomes will resonate far beyond the project’s duration, contributing to a global shift towards ethical and sustainable practices in the assessment of chemicals and materials.






